Print PDF version
Print PDF version
 Code BiteSize
Code BiteSize
There are a number of code related general awareness courses available for instance: Abrasive wheels, Eye Protection, PPE, and Ladder Safety.
Related UKRI code
Contents
Revisions
| 1 | Initial release | Sept 2012 |
| 1.1 | Amendments to training and audit sections | May 2013 |
| 1.2 | Minor changes to Appendix 2(h) | June 2014 |
1.3
| Add document retention Appendix
| December 2014
|
1.4
| Addition of motor vehicles to Appendix 2(2H) and
new Appendix 3 on Vibrating Equipment.
Minor change to Ladder Inspector training.
| February 2016
|
1.5
| Added Shelving and Racking Appendix
| November 2016
|
1.6
| Minor changes to Appendix 2B
| September 2017
|
1.7
| Minor change to Appendix 4 related to launch of SHE Assure
| October 2018
|
1.8
| Update to Appendix 2b to include kick-stools
| November 2020
|
1.9
| Minor update to wording of Appendix 2B for ladder standards
| September 2022
|
1. Purpose
Work at the STFC involves the use of a large amount of work equipment – ranging from simple access equipment to manufacturing robots.
Work with powered, electronically controlled and hand operated work equipment has the potential for serious personal injury and significant damage to property if the work equipment is not managed safely.
The STFC aims to pro-actively manage the risks associated with the selection, purchase, installation, use, modification, maintenance and repair of work equipment to minimise the potential for work equipment failures.
The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations (PUWER) 1998 impose specific legal duties on the STFC to provide, inspect, maintain and operate safe work equipment. Additional duties are imposed by:
- The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act, 1974.
- The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999.
- The Personal Protective Equipment at Work Regulations 1992 (as amended)
While this code addresses the general requirements to ensure that any item of equipment can be used safely, the appendices to this code outline controls for the management and use of specific types of equipment not covered in other codes, for example ladders, fume hoods (LEV’s), and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
2. Scope
This code applies to all work equipment used on STFC sites by employees, facility users, visitors, to work equipment owned by the STFC but used by others (for example tenants), and to work equipment used by STFC employees at non STFC sites in the course of undertaking Council business.
Contractors and tenants are responsible for ensuring that their own work equipment is safe to use and fit for purpose.
Related STFC SHE Codes include:
- STFC SHE Code 2: Safe Movement of Vehicles;
- STFC SHE Code 5: Incident Reporting and Investigation;
- STFC SHE Code 6: Risk Management;
- STFC SHE Code 9: Work at Height;
- STFC SHE Code 10: Provision of SHE Training;
- STFC SHE Code 11: Confined Spaces;
- STFC SHE Code 15: Management of Contractors;
- STFC SHE Code 17: Portable electrical Equipment;
- STFC SHE Code 19: Work on buildings, premises, services and infrastructure;
- STFC SHE Code 26: Safe use of lifting equipment and lifting accessories;
- STFC SHE Code 33: Safety of Pressure and Vacuum Systems; and
- STFC SHE Code 37: COSHH
3. Definitions
3.1 Work equipment
Work equipment covers almost any equipment used at work. For the purposes of this code work equipment can be considered “high risk” or “low risk”.
Low Risk work equipment includes but is not limited to the following examples:
- Portable battery tools;
- Hand tools;
- Sack trucks and gas bottle trolleys;
- Office equipment (photocopiers etc.);
- Smaller pieces of Laboratory equipment (analytical equipment etc.);
- Lifting equipment; and
- Access equipment (ladders, scaffolding etc.)
High Risk work equipment covers all those items that can present serious physical hazards when in use, and includes but is not limited to the following examples:
- Workshop-type equipment also called “machines” (lathes, pillar drills, milling machines, guillotines etc.);
- An installation, such as a series of machines connected together; and
- Work vehicles including but not limited to fork lift trucks, electric vehicles, MEWPS, cherry pickers etc. (excludes hire or personal cars, see SHE code 8).
It does not cover:
- Substances (e.g. acids, cement, water);
- Electrical equipment that is not ‘used’ in a physical manner ( e.g. computers, monitors, power supplies, lasers, battery chargers etc);
- Structural items (e.g. walls, stairs, roof , fences); and
- Private or Rented Cars and Vans.
3.2 Use of work equipment
Use of work equipment includes all activities involving that equipment, such as:
- Stopping or starting the equipment;
- Repair;
- Modification;
- Maintenance;
- Servicing;
- Cleaning;
- Training;
- Use; and
- Transportation.
3.3 Inspection of work equipment
A visual or more rigorous inspection by a competent person to identify whether the equipment can be operated, adjusted and maintained safely, and that any deterioration can be detected and fixed before it gives rise to unacceptable risks. If necessary, inspection includes testing in an appropriate manner.
3.4 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE means all equipment – including clothing protecting against the weather – which is intended to be worn or held by a person at work and which protects them against one or more risks to their health and safety, or any addition or accessory designed to do the same.
3.5 CE Mark
The CE mark is a symbol that when affixed (by a manufacturer) to a product indicates that the product complies with the relevant EU legislation. 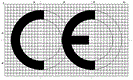
For equipment in the scope of this code (with three exceptions), it indicates that the equipment complies with the Essential Health and Safety requirements (EHSR’s) for that product, and may be considered safe to use in line with the manufacturer’s instructions. Consequently, all items of work equipment within the scope of this code, with three exceptions:
- Unpowered Hand tools;
- Access equipment; and
- Vehicles (fork Lift trucks, MEWPS, Cherry Pickers, bicycles).
Should carry the CE mark, including those imported from outside of the EU.
3.6 Hand tools
These are any portable tool, powered or requiring manual effort to use. Examples are: hammers, knives, handsaws, portable drills, hot air guns etc.
4. Responsibilities
4.1 Directors shall:
-
4.1.1 Ensure that the specification, design, fabrication, purchase, commissioning, operation, modification, maintenance, inspection and in-house repair of any work equipment is carried out by competent persons, and that sufficient resources are available to implement the requirements of this code.
4.2 Line Managers shall:
-
4.2.1 Ensure that any piece of work equipment used in areas for which they are responsible is fit for purpose and is used only for operations and under conditions for which it is suitable. An item of work equipment shall be designed and constructed in accordance with the relevant legislation, see Appendix 1, and if appropriate should carry the CE mark, see definitions.
-
- Work equipment that is designed and constructed completely “in-house” for use “in-house” should also be designed and constructed in accordance with relevant legislation. It does not need to be CE marked.
-
-
4.2.2 Ensure that significant risks arising from the use of work equipment are assessed and recorded; and control measures are put in place, see SHE Code 6: Risk Management. Appendix 3 outlines the particular hazards associated with prolonged use of vibrating equipment.
-
-
4.2.3 Ensure that work equipment is maintained in a safe state, in good working order and in good repair.
-
-
4.2.4 Ensure that a maintenance procedure and schedule is prepared for items of work equipment that require it. (E.g. hand tools will not require a documented procedure but a fork lift truck will).
-
-
4.2.5 Ensure that the work equipment is examined, inspected and tested with a frequency that is consistent with the risk assessment for that equipment but:
- where the safety of the work equipment is reliant on the installation conditions;
- Inspect after installation and before being put into service; or
- Inspect after assembly in a new location
- and if it is exposed to conditions causing deterioration that may result in dangerous situations;
- Inspect at suitable intervals and each time there is an incident involving the work equipment that may jeopardise its safety.
-
4.2.6 Ensure that records are kept of maintenance, examination, inspection and testing, including records of statutory inspections.
-
-
4.2.7 Ensure that all persons using work equipment are given appropriate information, instructions and training, see Appendix 5 and Appendix 6, and have sufficient experience; as appropriate have seen the risk assessment for the equipment or activity employing such equipment, and that they have supervision relevant to their level of expertise.
-
-
4.2.8 Ensure that a list of persons competent to use/maintain High Risk work equipment, see definitions, is displayed.
-
-
4.2.9 Ensure machinery is appropriately guarded in order to prevent contact with dangerous parts and protection is provided against specified reasonably foreseeable hazards e.g. swarf, temperature.
-
-
4.2.10 Ensure that, where identified by Risk Assessment, suitable PPE is supplied, and provision is made for its safe storage/cleaning and, as appropriate replacement.
4.3 Staff, tenants, facility users or visitors shall:
-
4.3.1 Ensure that they are familiar with the risk assessment for the task and follow the operating instructions for the work equipment that they are using. When using the equipment for a specialised or non-standard operation, consider whether the equipment is suitable and whether a separate risk assessment is required; and if so carry it out (see STFC SHE Code 6: Risk Management).
-
-
4.3.2 When using personal access equipment (harnesses/ropes etc.) –undertake their own inspection of such equipment - and any fall arrest or restraint equipment before each use.
-
-
4.3.3 Wear PPE as required, ensuring that it is suitably stored when not worn, and seek replacement at appropriate intervals and if damaged.
-
-
4.3.4 Undertake basic pre-use inspections of work equipment, as required by the planned work and the nature of the equipment. (E.G. A regular user of a CNC mill will need to spend a moment checking everything seems in order at the start of the working day, but more significant checks should be made before the first use of a neutron beam-line).
-
-
4.3.5 Report as an incident , following STFC SHE Code 5: Incident Reporting and Investigation, any instances where:
- An injury occurs whilst using work equipment; or
- A protective device (e.g. guard) or emergency stop mechanism fails to function when installed and used correctly.
4.4 SHE Group shall:
-
4.4.1 Ensure initial and refresher training for specific equipment items, as defined in Appendix 6, are made available for staff.
-
-
4.4.2 Provide assistance with interpretation of the requirements of this code.
-
-
4.4.3 Ensure that a register of ladders and step ladders is maintained, and that they are inspected
at regular intervals (at least annually) by a competent person.
5. References
Electronic copies of legislation, approved codes of practice and British Standards can be accessed by STFC staff through STFC-wide subscriptions for online information resources. These services are provided by the Chadwick and RAL libraries and further details can be found on the SHE Group website.
-
5.1 L22, Safe Use of Work Equipment (PUWER 98) ACoP (HSE)
-
-
5.2 L25, Personal Protective Equipment at Work ACoP (HSE)
-
-
5.3 Controlling airborne contaminants at work: A guide to local exhaust ventilation (LEV) HSG258
-
-
5.4 Working at height: A brief guide
INDG401
-
-
5.5 Safe use of ladders and stepladder: A brief guide
INDG455
-
-
5.6 Safety in the use of abrasive wheels HSG17
-
-
5.7 Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulations 2008
-
-
5.8 National Access and Scaffolding Confederation (NASC) - SG series of guidance documents.
-
-
5.9 BS EN 14175 – 2: 2003: Fume Cupboards. Safety and Performance Requirements
-
-
5.10 HSG6 “safety in working with lift trucks”
-
-
5.11 BGI/GUV-I 5139 E, Information Guide “Manufacturing and Operation of equipment designed for Research Purposes”